Kotlin Data Structure: Queue
Welcome to this post.
This is the second post about data Structure.
In this post, we are going to learn about Queue data structure.
In the previous post, we discuss Stack. Stack is FILO type data structure.
But Queue is the FIFO data structure, that means the data enter first that also come first.
In queue, to data in the queue, the method is called enqueue()
and to get data from queue, the method is dequeue()
Implementation of Queue:
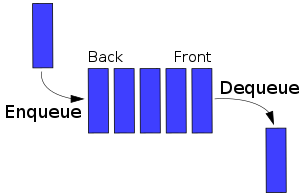
In the above picture, you can see that data inserted in the back or last position and then the position move one row. and the same thing happens when we access data.
So we have to track
This is the second post about data Structure.
In this post, we are going to learn about Queue data structure.
In the previous post, we discuss Stack. Stack is FILO type data structure.
But Queue is the FIFO data structure, that means the data enter first that also come first.
 |
| Src: Wikipedia |
and to get data from queue, the method is dequeue()
Implementation of Queue:
In the above picture, you can see that data inserted in the back or last position and then the position move one row. and the same thing happens when we access data.
So we have to track
- Top position
- Last position
Create an array of Int' and also create 2 variable that mentions above.
Methods:
enqueue():
insert data in the tail position and increase the tail
get data from head position index from the array and increase the head
if head and tail is same then the stack is empty
Now time for access data:
First, create the main method:
just run a for loop from 0 to 10 and insert data
dequeue()
run a while loop until the queue is empty
It's work fine.
That's is the basic queue implementation.
You can check this out on Github
Discussion about queue:
The uses of the basic queue are not huge. It has a very limited use.
Because it wastes memory.
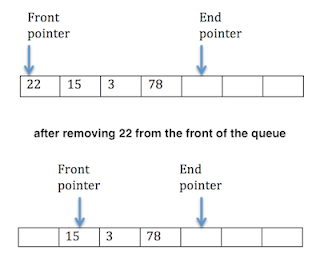
For example, if the queue has the capacity of 100. Then at the beginning data inserted from zero, when we access data from one we can get that data from the zero position. After the head is also increased and the tail already increased. Imagine by this way at 99 position data is filled and we access data from the 99 potions. If we want to insert new data into the queue it shows you a warning, "hey! I am full, I can not take any new data". But already the previous position is empty and there is no way to insert new data in the queue. we can use the previous position. But it allocates the memory. This is obviously the waste of memory. see the picture for the more clear concept.
To fix this problem we use the circular queue
In circular queue top position and the last position move around a circle. I will discuss circular queue in the next post.
Until then, stay happy and keep practicing.
Thank you for reading this post.
Happy coding
var ints = IntArray(10) var head = 0 var tail = 0
Methods:
enqueue():
insert data in the tail position and increase the tail
fun enqueue(n: Int) { ints[tail] = n tail += 1 println("Input:" + n) }dequeue():
get data from head position index from the array and increase the head
fun dequeue(): Int { val n = ints[head] head += 1 return n }Empty check:
if head and tail is same then the stack is empty
val isEmpty: Boolean get() = head == tail
Now time for access data:
First, create the main method:
fun main(arg: Array<String>) {
}
enqueue():just run a for loop from 0 to 10 and insert data
for (i in 0..9) { enqueue(i) }Output:
Input:0 Input:1 Input:2 Input:3 Input:4 Input:5 Input:6 Input:7 Input:8 Input:9works fine.
dequeue()
run a while loop until the queue is empty
while (!isEmpty) { println("value: " + dequeue()) }Output:
value: 0 value: 1 value: 2 value: 3 value: 4 value: 5 value: 6 value: 7 value: 8 value: 9
It's work fine.
That's is the basic queue implementation.
You can check this out on Github
Discussion about queue:
The uses of the basic queue are not huge. It has a very limited use.
Because it wastes memory.
For example, if the queue has the capacity of 100. Then at the beginning data inserted from zero, when we access data from one we can get that data from the zero position. After the head is also increased and the tail already increased. Imagine by this way at 99 position data is filled and we access data from the 99 potions. If we want to insert new data into the queue it shows you a warning, "hey! I am full, I can not take any new data". But already the previous position is empty and there is no way to insert new data in the queue. we can use the previous position. But it allocates the memory. This is obviously the waste of memory. see the picture for the more clear concept.
 |
| Queue Data structure |
To fix this problem we use the circular queue
 |
| Circular Queue |
In circular queue top position and the last position move around a circle. I will discuss circular queue in the next post.
Until then, stay happy and keep practicing.
Thank you for reading this post.
Happy coding





No comments :